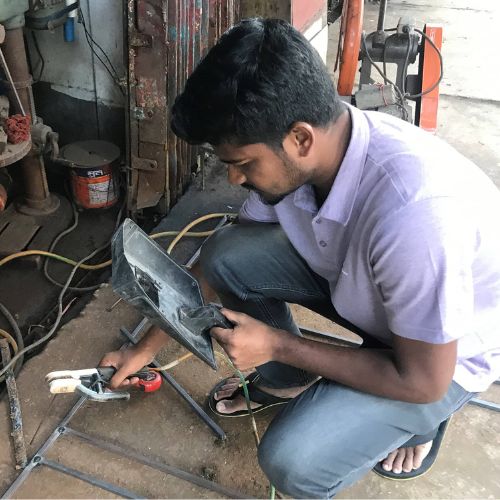
Tungsten, a robust and versatile metal known for its exceptional melting point, has long been an indispensable element in various industries. Among its varied of use, Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding method stands out as one of the most crucial user.
As TIG welding requires precise control and excellent heat resistance, the choice of tungsten is crucial to ensure successful welds with optimal strength and quality.
In this article, we will explore the different types of tungsten available for TIG welding and delve into their unique properties and advantages. By understanding these variations, welders can make decisions that enhance their welding processes to achieve superior results and also can choose best tungsten for better weld quality .
Types of Tungsten

1. Pure Tungsten (Green-tipped):
Pure tungsten offers general-purpose welding for most metals, except aluminum. Tungsten and performs best in AC/DC welding applications. It is also the most economical of all tungsten electrodes.

a. Benefits of pure tungsten electrodes Advantages:
- Highest current carrying capacity
- General-purpose welding for most metals, except aluminum
b. Recommended applications and industries for pure tungsten electrodes:
- Maintenance & repair work for general-purpose welding
- Light fabrication and production welding in mild steel, stainless steel, nickel alloys, and titanium
2. Thoriated (2%Red tipped, 1% yellow, 3% purple):
Thoriated tungsten electrodes contain a small amount of thorium oxide and are available in various shades of red, yellow, and purple.

a. Benefits of thoriated tungsten electrodes
- Higher current carrying capacity& Superior arc starting characteristics
- Longer electrode life than pure tungsten electrodes.
b. Recommended applications and industries for thoriated tungsten electrodes
- Maintenance & repair work for DC welding
- Light fabrication and production welding in steels, stainless steel, nickel alloys, titanium, and other metals
3. Ceriated 2% (Grey tipped):
Ceriated tungsten has a low level of thorium oxide content and offers good arc stability and strike characteristics. This type of tungsten is ideal for welding aluminum alloys.

a. Benefits of Ceriated 2% (Grey tipped):
- Low level of thorium oxide content & Ideal for welding aluminum alloys
- Can be used in both AC and DC welding applications.
b. Recommended applications and industries for creating 2% tungsten electrodes
- Maintenance & repair work for general-purpose welding
- Light fabrication and production welding in aluminum alloys, steel, stainless steel, titanium, and nickel alloys
4. Lanthanated (1.3-1.7% Gold tipped, black 0.8-1.2%, blue 1.8-2.2%):
Lanthanated tungsten has a slightly lower current carrying capacity than pure tungsten.
a. Benefits of Lanthanated (1.3-1.7% Gold tipped, black 0.8-1.2%, blue 1.8-2.2%):
- Higher current carrying capacity than pure tungsten
- Low burn-off rates for aluminum and magnesium alloys.
b. Recommended applications and industries for Lanthanated (1.3-1.7% Gold tipped, black 0.8-1.2%, blue 1.8-2.2%)
- Maintenance & repair work for AC/DC welding
- Light fabrication and production welding in steel, stainless steel, nickel alloys, aluminum alloys, titanium, and other metals
5. Zirconiated (0.7%- 0.9% White-tipped, brown 0.15-.5):
Zirconiated tungsten offer good arc stability and low burn-off rates for aluminum and magnesium alloys.
a. Benefits of Zirconiated (0.7%- 0.9% White-tipped):
- Ideal for welding aluminum and magnesium alloys
- Can be used in all AC welding applications.
b. Recommended applications and industries for Zirconiated tungsten electrodes
- Maintenance & repair work for general-purpose welding
- Their contamination resistance makes them ideal for nuclear power plant welding, ensuring defect-free welds on stainless steel and other alloys used in construction.
6. Rare Earth (Purple tipped):
Rare earth tungsten electrodes contain a combination of rare earth oxides, such as cerium, lanthanum, and yttrium.

a. Benefits of Rare Earth (Purple Tipped):
- Higher current carrying capacity than pure tungsten
- Ability to withstand higher temperatures
b. Recommended applications and industries for Rare Earth (Purple Tipped):
- Maintenance & repair work for AC/DC welding
- Light fabrication and production welding in aluminum, titanium, copper, brass, steel, stainless steel, and nickel alloys.
Tungsten Electrode Performance (Chart)
| Base Metal | Purpose | Shielding Gas | Current Flow | Electrode Type | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | Argon | AC | Pure | Balls Easily & Tends to split in high current | |
| Aluminum & Magnesium Alloy | General | Argon | DC | Zirconiated | Good toughness, better arc stability and doesn’t split |
| General | 75% Argon, 25% Helium | DC | 2% Thoriated | Higher arc range, better stability with lower split chance. Medium erosion. | |
| General | 75% Argon, 25% Helium | DC | 2% Thoriated | Higher arc range, better stability with lower split chance. Medium erosion. |
| Aluminum & Magnesium Alloy | Controlled Penetration | Argon & Helium | DC | 2% ceriated (EW-CE2 | Wide current range, best arc start and stability and lowest erosion rate |
| Aluminum & Magnesium Alloy | Increased Penetration | 75% Argon & 25% Helium | DC | 2% Thoriated | Good arc start, medium tendency to split, low erosion rate & best stability in medium current |
| Increased Penetration | Helium | DC | 2% ceriated (EW-CE2 | Wide current range, consistent arc state, no splitting in ac or dc, and low erosion rate |
| General | 75% Argon & 25% Helium | Dc | 2% Thoriated | Good arc start, best stability & medium chance to split | |
| General | 75% Argon & 25% Helium | DC | 2% ceriated | Low erosion, wide current range, consistent arc and good stability. | |
| Copper & Nickel Alloy | Control penetration | Argon | AC | Zirconiated | Split on start, rapid erosion at high current flow |
| Increased penetration | 75% Argon, 25% Helium | DC | 2% ceriated | Low erosion, wide current range, no splitting and consistent arc. | |
| Increased penetration | 75% Argon, 25% Helium | DC | 2% ceriated | Low erosion, wide current range, no splitting and consistent arc. |
Conclusion
Tungsten electrodes are essential for TIG welding and come in several different types, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Pure tungsten is best suited for DC welding applications, while lanthanide, zirconiated, and rare earth tungsten electrodes are suitable for both AC and DC welding.
Each type of electrode offers its own advantages in terms of arc stability, current carrying capacity, and burn-off rates. Depending on the material being welded and the welding application, certain tungsten electrodes may be more suitable than others. For example, to weld 1/16 inch aluminum, you should choose one type of aluminum and for 1/2 inch aluminum weld the requirements differs.
