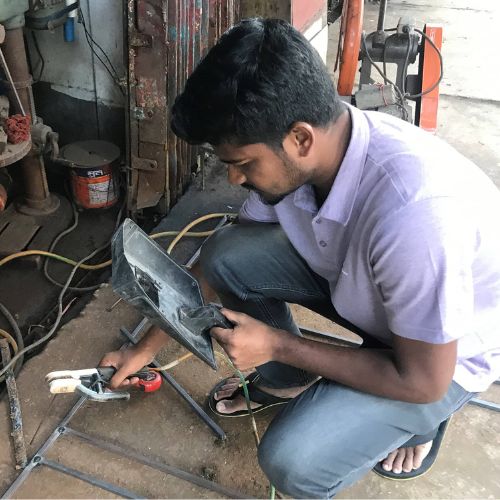
Different power sources are involved in the welding processes, which might confuse you. Sometimes, choosing the wrong arc welding power source can be the prime reason behind welding defects, overheating, and even some significant issues!
So today, I’ll guide you through CC vs. CV welding, as most beginners aren’t friendly with their characteristics and differences.
Read on to find out.
What Is The Difference between Cc and Cv Welding?
CC generates a lower current change when welding materials, while the CV tends to produce a larger current change during a weld.
Constant Voltage is basically involved in the self-regulating welding process. On the other side, the Constant Current is mostly involved in manual processes.
Due to the reduced current change, CC is friendly with welding thin materials. At the same time, CV is compatible with thick materials for its enhanced current changes.
Constant Current ensures more precision, while Constant Voltage ensures cost-efficiency.
CC Welding
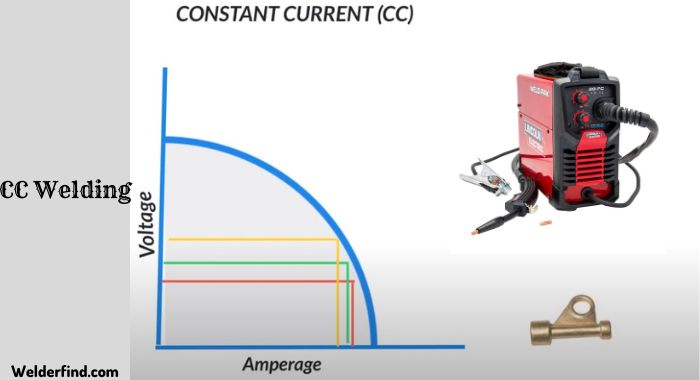
Constant Current, also known as CC, is known to be a specific power source of arc welding. From a relatively large voltage output, cc generates a lower current change of welding, making it suitable for welding through thin materials.
How Works CC Welding?
As you know, cc welding generates a constant current for welding. This can be done by utilizing a particular transformer, which will assist in controlling the overall welding current.
So, even if you find the arc Voltage fluctuating, the welding Current will be able to maintain consistency!
What is the Advantage and Disadvantage of Using a CC Welding?
Both pros and cons are noticeable if you use a cc-power source for welding materials. Some of them are as follows:
Advantages:
- Constant Current helps you avoid burn-throughs as the current will maintain consistency instead of increasing dramatically.
- CC offers excellent control to ensure precision during a weld. As a result, it’s an ultimate go-to for those projects where precision matters a lot, like welding thin metals.
- Since the welding Current will maintain as much consistency as needed, cc usually doesn’t cause any defects regarding welding.
Disadvantages:
- Compared to constant Voltage (CV), it’s going to be a little more costly.
- Constant Current isn’t the best choice for welding thicker materials.
- For beginners, it might be a tad bit complex using the constant Current.
CV Welding
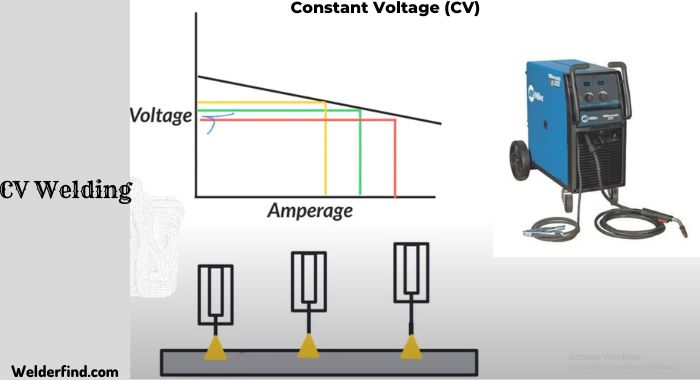
Just like the CC, CV or Constant Voltage is another arc welding power source. But unlike the constant Current, CV tends to generate a comparatively large current change of welding.
This makes it better for welding through stainless steel, aluminum, and such high-melting components.
How Works CV Welding
Sometimes, welders consider CV an inverter for transforming DC (Direct Current) into AC (alternating Current).
It is mainly involved in self-regulating processes, offering extended heat required to melt thicker metals quickly and precisely.
What is the Advantage and Disadvantage of Using a CV Welding?
It is no exception to the constant Current when it comes to pros and cons. So here, I’ve listed a couple of them given below:
Advantages
- Constant Voltage is well-known for affordability and offering Voltage and current stability.
- Compared to the constant Current, CV is known to be more cost-efficient.
- There will be less chance of premature electrical failure and overheating issues as the CV maintains consistency in keeping the voltage ideal.
Disadvantages
- Since the constant Voltage produces a large welding current than the cc, it shouldn’t be your optimum choice for welding thinner metals.
- Sometimes, it’ll be a wee bit tough to maintain precision because the CV is involved in a self-regulating process, where welders can’t always get the freedom of controlling the overall procedure.
Which Is Better, CC or CV Welding?
It isn’t going to be fair to consider a single winner between the CC and CV. Ask why? Because they both have their specialties with some limitations, which you can’t overcome, to be very honest!
For instance, a constant current is the better choice for those who require precision and consistency for welding thinner materials. But it’s equally true that CC might be a little pricier than the CV.
On the flip side, Constant Voltage ensures consistency in maintaining the Voltage. Meaning there will be less chance of ending up with overheating issues while welding thicker objects.
But unfortunately, it sometimes lacks accuracy than the CC for being self-regulated.
Last Words
Through the cc vs cv welding comparison, I tried to give you a complete idea of their features, how they work, and some of their common dissimilarities.
Following that, I discussed why they both stand out in their own ways. So decide upon your needs and preferences.
FAQ
Is MIG welding CC or CV?
In a word, Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding is CV as it incorporates only a constant voltage output.
Is SMAW CC or CV?
Unlike the MIG, Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) requires constant Current for being a manual process of arc welding.
