Generating perfect welding is not a cup of tea. Different forms of welding require users to follow different processes. Among them, TIG welding is one of the most used procedures.
Do you know What is TIG welding and how does it work? TIG welding is a welding procedure to join various metal parts through the welding current. The entire procedure works through various components. Among them, a power source, welding torch, tungsten Electrodes, filler metal and Shielding gas are most vital ones.
If you want to dig more into TIG welding and its working process, go through the entire article.
What is TIG Welding?
Gas tungsten arc welding, commonly familiar as TIG welding refers to an arc welding process. It utilizes a non-consumable electrode consisting of tungsten to produce an arc that joins metal. In short, TIG Welding is a welding process that people use to join different metal parts through the welding current.
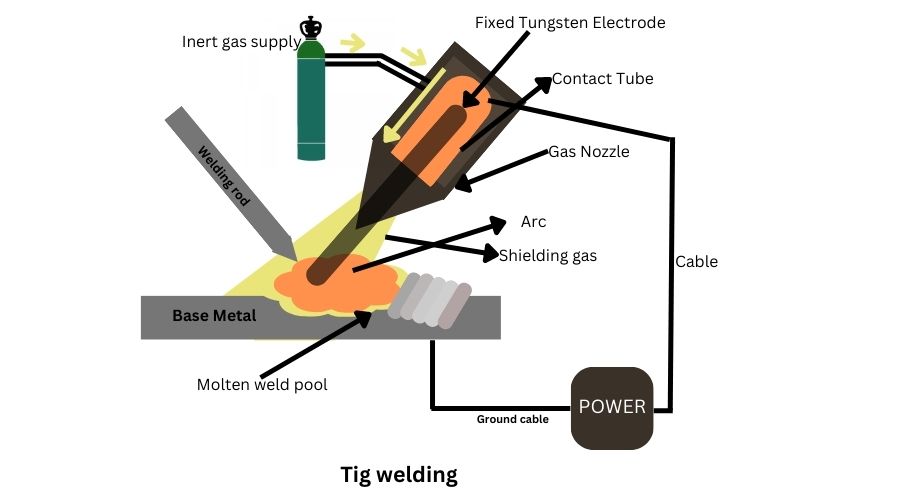
The process involves a power source, welding torch, tungsten Electrodes, and Shielding gas. The shielding gas consists of either pure argon or argon-helium mixture. Initially, helium was used as the main shielding gas. That’s why, the process was initially familiar as Heliarc.
The welding torch includes a tungsten electrode. This electrode features the highest melting point compared to other metals involved in the process. The inert gas flows through the welding torch to prevent oxidation and create tiny circular holes in the metals. The process can use either a direct current or an alternating current, based on the metals.
During the 1940s, the process got momentum to join Aluminum and Magnesium. Now it has widespread use in the following areas:
- Pipeline construction
- Container construction
- Portal construction
- Aerospace.
What are the advantages of TIG Welding?
TIG welding has several advantages. Here are the most prominent ones:
- It offers more accurate outcomes.
- TIG welding is a more environment-friendly process than other welding processes. The argon gas is comparatively safe for the environment and the process creates less smoke. So, there is less chance of air pollution.
- The process leaves the welder with full control over the heat generation.
- People can weld multiple materials and alloys through the Tig welding method.
- It doesn’t require purchasing multiple shielding gases for efficient work.
- It offers more customizable options for perfect welding.
What are the disadvantages of TIG Welding?
- The TIG welding method is more costly compared to other welding methods.
- TIG welding requires more knowledge, skills and expertise for better results.
- Tig welding is a type of welding process that is time-consuming compared to other processes.
- Welders must remember the appropriate polarity for efficient welding
- Welders must ensure a wind-free environment to avoid oxidation which is very tricky to maintain.
What are the key elements of TIG welding?
TIG welding involves several components that work together to produce the desired outcome. Therefore, it is crucial to know about the components of TIG welding before knowing the working process. Let’s explore the functions of these components before going to the working process.
Non-Consumable Tungsten Electrode

There is a non-consumable tungsten electrode in the welding torch. Manufacturers use tungsten as this metal features a high melting point than other metals. The melting point of stainless steel is between 1400 and 1530°C, whereas the melting point of tungsten is approximately 3422°C.
As a result, the tungsten electrode will not burn during the welding process. However, the tungsten electrode may erode due to other factors in the process.
Users will find a variety of Tungsten electrodes to insert into the welding torch. The following tungsten are the most used ones:
- Pure Tungsten
Pure tungsten is one of the most used tungsten while welding Aluminum alloys and magnesium . This tungsten is the cheapest, easy to control, and provides excellent arc stability. However, they are not favorable to DC welding and have a lower capacity to transport the current.
- Lanthanated Tungsten
Lanthanated Tungsten consists of lanthanum oxide and has many similarities with Thoriated Tungsten. They feature outstanding current-carrying efficiency and erode slowly. But they are not as efficient as Thoriated Tungsten. This tungsten is also familiar as the Gold Tip.
- Thoriated Tungsten
The current transporting capacity of Thoriated Tungsten is top-notch. Besides, they are convenient for maintaining the tip’s shape. These electrodes consist of 1 to 2 percent of thorium oxide. But they release alpha (radioactive material) that poses severe risks to the human respiratory system.
- Ceriated Tungsten
Ceriated Tungsten consists of cerium oxide. This tungsten is durable and offers excellent arc stability. Users generally use it to weld steel, nickel, stainless steel, and titanium. However, this one also has less ability in transferring current.
- Zirconiated electrodes:
Zirconiated electrodes consist of tungsten and zirconium oxide. One of the key features of this electrode is that they produce extremely high-quality output. Besides, they are durable and have higher quality to prevent contamination.
2.Inert Gas

Inert gas is one of the key components of the welding process. It consists of Argon gas. However, users often use an argon-helium mixture or argon-hydrogen mixture as inert shielding gas.
Shielding gas is vital to safeguard the weld puddle from the oxidation process. It also protects the weld pool from atmospheric impurities. However, which Shielding gas one will use depends on the materials to be welded.
- Argon:
Users use it to weld materials like steel, aluminium, stainless steel, and titanium.
- Argon-hydrogen mixture:
This gas mixture generates a clean-looking weld while preventing oxidation in the welding surface.
- Argon-helium mixture:
Argon-helium mixture elevates the arc’s temperature. Therefore, it raises the welding speed and promotes weld penetration.
3.Welding Torch

A welding torch refers to a tool for dissolving and blending metals. These tools are mainly available in two forms: Air-cooled TIG torches and Water-cooled TIG torches.
- Air-cooled TIG torches: People use these torches for minor projects or working with thin metals. They have a tendency of overheating and feature one gas input.
- Water-cooled TIG torches: People use this torch in big projects that have quick cooling -requirements. The torch has one input for gas, one for water lines and another output for water lines. The torches are generally more expensive than the previous one due to their water-cooling system.
4.Power source
TIG welding requires a constant source of current for consistent and stable heat input. The source either be DC or AC based on the material and desired output. In TIG welding, DC power always uses the negative polarity to avoid excessive heating and melting.
In contrast, AC power utilizes the alternating current between the negative and positive polarities to sustain heat while preventing the overheating of the base materials.
5. Filler Metal

In the TIG welding process, welders can use filler metals to join metals or do the job without any filler metal. The arc of the tungsten electrode will do the task of melting metal bases and later fuse them together. However, filler metal generates strong joints while avoiding any cracks.
Moreover, the task of adding filler metal in the TIG welding is not an easy task. The welders need to use one hand to control the TIG torch while placing filler wire with another hand into the weld pool. So you need to be very careful using filler metal in tig welding.
How does TIG welding work?
The main mechanism of the TIG process is to melt down the base metals through the electrical arc. TIG welding uses current to produce a short circuit (arc) between a tungsten electrode and the metal. The tungsten electrode is non-consumable and works as the positive anode. The metal that you will weld works as the negative cathode. The process can use either direct currents (DC) or alternating currents (AC) based on the materials.
Since tungsten has a high melting temperature, it will not burn when the temperature of the entire system increases. Instead, it will work as a connector between the arc and metals to weld them. Furthermore, the welding torch supplies shielding gas that consists of argon to prevent oxidation.
Application of TIG
- Almost every sector of industry applies the TIG welding process. But it is mostly used in precision welds for generating high-quality welding.
- The TIG process is mostly used in fusing exotic metals as it installs complete control over the heat input. Examples include stainless steel, aluminum, magnesium, nickel alloys, etc.
- Mechanized systems also use the TIG welding process with filler wire or autogenously
- The process has widespread applications in pipeline construction.
TIG or Stick or MIG which one is best?

TIG, Stick and MIG are some of the most used welding processes in the industrial area. However, these methods differ from each other in various aspects and produce different outcomes.
Therefore, the selection of the right process depends on the material and your preferred outcome. So, it is vital to know the key features of these processes for the right choice of welding process to achieve the desired outcomes.
Key features of MIG Welding
- The MIG welding process uses an electric arc to generate heat, melt the base materials and then join the joints. MIG welding involves the passage of filler wire and shielding gas via the welding gun.
- Speed, flexibility and minimum clean-up are the key characteristics of this method.
- It is one of the most common welding methods by manufacturing professionals and custom automation
- Professionals utilize MIG welding to weld materials, such as Stainless Steel, Aluminum Alloy and Mild Steel.
Key features of TIG Welding
- TIG welding or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to melt the materials and join them.
- Unlike MIG, TIG welding requires hands to apply the filler wire.
- Professionals use the TIG welding process for Aluminum Alloys, Stainless Steel, Chromoly, Titanium, Copper, etc.
- The TIG process is famous for producing high-quality, clean-look finishing for thinner metals.
- It requires no cleanup and can weld various metals of different sizes.
Key features of Stick Welding:
- Stick or Shielded Metal Arc Welding is the most elementary form of welding and is easy to learn.
- Stick welding needs no shielding gas.
- The process utilizes an electrode “stick” instead of a gun
- It is a more suitable welding process for thicker metals.
- It has widespread applications on ships, home construction and other heavy construction development.
- It is appropriate to weld materials like Stainless Steel, Cast Iron, Steel
Final verdict
The TIG welding process is a trickier welding method that requires knowledge and skills. Many people lack proper knowledge about Tig and its working process.
Therefore, this article has solely focused on “What is TIG Welding and how does it work?” I hope the in-depth information will help the readers in achieving perfect welding.
